Rosacea: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention - Dr Yeung Ho Hong 楊浩康
Rosacea: Symptoms, Types, and Treatment Management
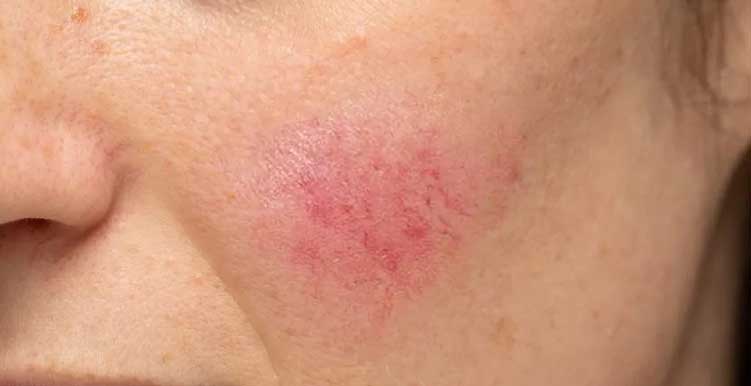
Rosacea is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. Patients may experience persistent redness, recurring rashes, papules, and even pustules. Many individuals mistake rosacea for acne, leading to the use of inappropriate treatments that can worsen symptoms. The onset of rosacea is associated with multiple factors, including genetic predisposition, sun damage, heightened vascular reactivity, and emotional stress. These factors collectively influence skin vasodilation and immune responses, ultimately causing abnormal reactions in facial skin.
Types of Rosacea
Clinically, rosacea is classified into four types. The most common type is characterized by central facial redness and visible fine blood vessels, often accompanied by dry and sensitive skin. This type typically involves only mild inflammation. The second type builds on redness with the addition of papules and pustules, and patients often report localized burning or stinging sensations, significantly impacting both appearance and comfort. The third type, known as rhinophyma or granulomatous rosacea, is usually confined to the nose or cheeks, where the skin thickens, displaying crater-like depressions and surrounding congestion. Over time, this can lead to tissue deformity. The fourth type, ocular rosacea, though rare, affects the eyes and may present with mild redness and burning, potentially impairing vision. Early professional intervention is critical for this type to prevent complications.
Many patients harbor misconceptions about rosacea, commonly mistaking it for teenage acne or pimples. Unlike acne, which is primarily caused by clogged hair follicles, excess oil, and bacterial infections—manifesting as comedones and pustules—rosacea involves persistent vasodilation and skin inflammation. Some patients also believe that all corticosteroid creams are a cure, but prolonged use can thin the skin and cause a rebound effect, necessitating cautious application.
Treatment and Care Practices
Treatment approaches vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. For mild cases, topical treatments such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, and brimonidine can effectively reduce redness and inflammation. For more severe cases with pustules, oral antibiotics like doxycycline or metronidazole may be prescribed. Additionally, for persistent facial redness, laser therapy has been proven to improve vascular conditions in the skin and reduce the extent of erythema.
Beyond medication, daily skincare and lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in managing the condition. Patients should avoid spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeinated beverages, as these can stimulate the skin and exacerbate inflammation. Opting for hypoallergenic cosmetics and skincare products with minimal additives can help prevent allergic reactions and further damage. Sun protection is essential—patients should avoid sun exposure and use high-SPF sunscreen and physical barriers like hats to prevent worsening of symptoms.
Regular facial cleansing, keeping the skin dry, and maintaining appropriate hydration are also vital care practices. Gentle cleansers and moisturizers help preserve the skin’s natural barrier, reducing irritation and inflammatory responses. Moreover, managing emotions and alleviating stress can improve the condition, as emotional fluctuations often trigger vasodilation and symptom flare-ups. Patients may benefit from joining support groups or seeking psychological counseling, which can enhance both visual and emotional well-being.
A clinical case illustrates these points: a middle-aged woman mistakenly treated her condition as acne, using improper methods that led to recurrent flare-ups. After a detailed diagnosis by a dermatologist, she switched to a rosacea-specific treatment plan combining topical creams, laser therapy, and lifestyle and skincare adjustments. Her symptoms improved significantly, and her skin condition stabilized. Such cases underscore the importance of accurate diagnosis and evidence-based treatment.
In summary, rosacea is a relatively common chronic inflammatory skin condition that may resemble acne in appearance but differs fundamentally in its causes and treatment strategies. By correctly understanding the disease, selecting appropriate treatments, and adopting lifestyle changes, patients can effectively manage symptoms, prevent recurrence, and improve their quality of life. Guidance from healthcare professionals and comprehensive care are key to managing rosacea, empowering patients to face this condition with greater confidence and positivity.
