Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
by Dr Yeung Ho Hong (楊浩康)
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. It occurs when there is an accumulation of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints. This condition has been known for centuries and is often associated with a diet rich in purines.
www.scientificanimations.com/, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
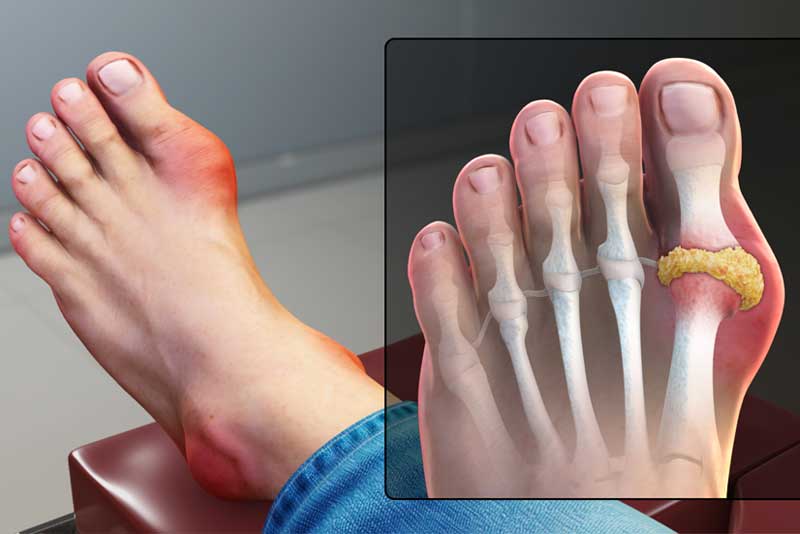
Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by hyperuricemia, which is an excess of uric acid in the blood. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- *Diet:* Foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and sugary beverages, can increase uric acid levels.
- *Obesity:* Excess body weight can lead to increased uric acid production and decreased excretion.
- *Genetics:* A family history of gout can increase an individual's risk.
- *Medications:* Certain diuretics and medications that affect kidney function can elevate uric acid levels.
- *Medical conditions:* Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease can also contribute to gout.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout attacks typically occur suddenly and can be extremely painful. Common symptoms include:
- *Intense joint pain:* Often starting in the big toe, but can affect other joints like the ankles, knees, and wrists.
- *Redness and swelling:* The affected joint may appear red and swollen.
- *Limited range of motion:* The joint may become stiff and difficult to move.
- *Fever:* In some cases, a mild fever may accompany a gout attack.
Diagnosis of Gout
A healthcare provider can diagnose gout based on the following methods:
- *Medical history:* A discussion of symptoms and family history.
- *Physical examination:* Checking for signs of inflammation in the joints.
- *Blood tests:* Measuring uric acid levels in the blood.
- *Joint fluid analysis:* Extracting fluid from the affected joint to identify uric acid crystals.
Treatment and Management
While gout can be a chronic condition, there are effective treatments available to manage symptoms and prevent future attacks.
Acute Attack Management
- *Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):* Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- *Colchicine:* This medication can reduce pain during acute attacks, especially if taken early.
- *Corticosteroids:* These may be prescribed if NSAIDs or colchicine are not effective or suitable.
Long-term Management
To prevent future gout attacks, long-term strategies include:
- *Lifestyle changes:* Maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly can help manage uric acid levels.
- *Dietary modifications:* Reducing intake of purine-rich foods and avoiding alcohol can lower the risk of gout attacks.
- *Medications:* In some cases, medications such as allopurinol may be prescribed to lower uric acid levels over time.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful and often debilitating condition, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can lead healthy lives. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. If you suspect you have gout, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
